Have you ever wondered why certain metals are grouped on the left side of the periodic table? Understanding this can unlock secrets about how these metals behave and why they are so important in everyday life.
If you’re curious about what makes these metals special and how they differ from others, you’re in the right place. Keep reading, and you’ll discover the surprising reasons behind their position and what that means for you.

Credit: elementsandtheperiodictable.weebly.com
Position Of Metals On The Periodic Table
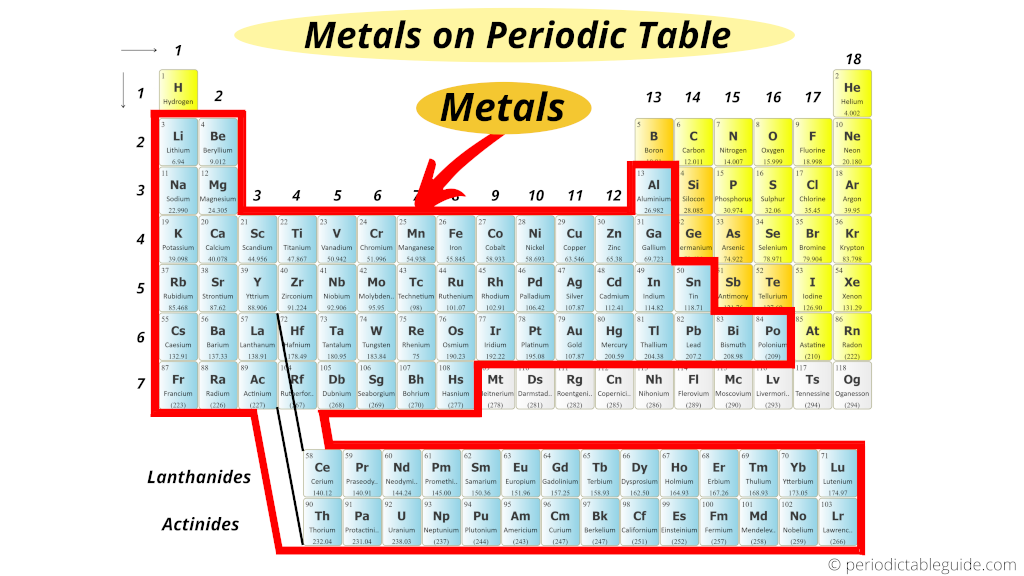
Metals occupy a large part of the periodic table. They are mostly found on the left side and in the center. This position helps identify their properties and behavior.
The periodic table arranges elements by atomic number. Metals appear in groups 1 through 12 and some in groups 13 to 16. Their location shows their strong ability to lose electrons and conduct heat and electricity.
Location Of Alkali And Alkaline Earth Metals
Alkali metals sit in group 1 on the far left. These metals are very reactive and soft. Next to them, in group 2, are alkaline earth metals. They are harder and less reactive but still good conductors.
Transition Metals In The Center
Transition metals fill groups 3 to 12. They are found in the table’s middle section. These metals are dense, strong, and have high melting points. Their position explains their varied uses in industry.
Metalloids And Metals Boundary
Metalloids lie along a zigzag line separating metals from nonmetals. Metals are to the left of this line. This boundary shows the gradual change from metallic to non-metallic properties.
Characteristics Of Left-side Elements
The elements on the left side of the periodic table have unique traits. These traits make them stand out from other elements. Most of these elements are metals. Their properties affect how they react and combine with other substances.
These metals are very important in science and daily life. They often lose electrons easily, forming positive ions. This behavior shapes many of their chemical reactions and uses.
Physical Properties Of Left-side Elements
Left-side elements are usually shiny and solid at room temperature. They are good conductors of heat and electricity. These metals are also ductile, meaning they can stretch into wires. They tend to have high melting and boiling points. Their density varies but is generally lower than metals on the right side.
Chemical Behavior Of Left-side Elements
These elements react quickly with water and oxygen. They lose electrons to form positive ions easily. This makes them very reactive metals. They often form basic oxides. Their compounds usually have simple formulas and clear colors.
Common Uses Of Left-side Metals
Left-side metals are used in many everyday items. They are found in batteries, construction materials, and electronics. Their reactivity helps in making strong alloys. These metals also play a key role in manufacturing and energy production.
Types Of Metals Found On The Left
The left side of the periodic table holds some of the most reactive and interesting metals. These metals share common traits like softness and high reactivity. They play important roles in everyday life and industry. Two main groups stand out here: alkali metals and alkaline earth metals. Each group has unique features and uses.
Understanding these metals helps us appreciate their place in chemistry and daily life.
Alkali Metals
Alkali metals include lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium. They are very soft and can be cut with a knife. These metals react quickly with water to produce hydrogen gas and a strong base. They have low melting points compared to other metals. Alkali metals are shiny and good conductors of electricity. They are used in batteries, fireworks, and medicines.
Alkaline Earth Metals
Alkaline earth metals include beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium. They are harder than alkali metals and less reactive. These metals also react with water, but slower and less violently. They have higher melting points and are denser. Alkaline earth metals are important in making alloys, fireworks, and medicines. Calcium, for example, is vital for bones and teeth.
Comparison With Nonmetals And Metalloids
Comparing metals on the left side of the periodic table with nonmetals and metalloids reveals clear differences. Each group has unique traits that set them apart. Understanding these differences helps explain their roles in nature and industry.
Metals tend to lose electrons and form positive ions. Nonmetals usually gain electrons and form negative ions. Metalloids show mixed behavior, acting like metals or nonmetals depending on conditions.
Physical Properties
Metals on the left are shiny and good conductors of heat and electricity. They are also malleable and ductile, meaning they can bend without breaking. Nonmetals lack shine and do not conduct electricity well. Most are brittle solids or gases at room temperature. Metalloids have properties between metals and nonmetals. For example, they may conduct electricity but not as well as metals.
Chemical Behavior
Left-side metals react easily with other elements, especially nonmetals. They tend to form ionic compounds by losing electrons. Nonmetals gain or share electrons, forming covalent bonds. Metalloids can behave like metals or nonmetals in reactions. This makes their chemistry more complex and varied.
Common Uses
Metals on the left serve in construction, wiring, and tools due to their strength and conductivity. Nonmetals are vital in life processes and industries, like oxygen for breathing and carbon in fuels. Metalloids find use in electronics, thanks to their semi-conducting abilities. Silicon, for example, is key in computer chips.
Exceptions And Special Cases
Most metals are found on the left side of the periodic table. They share many common properties like good conductivity and malleability. Still, some elements do not follow these typical patterns. These exceptions and special cases are important to understand.
They show that the periodic table is not just a simple list. It is a system with complex rules and unique elements. Some non-metals appear near metals, and some metals act differently. These special cases help scientists learn more about element behavior.
Metalloids: The Boundary ElementsMetalloids sit between metals and non-metals on the table. They have mixed properties. For example, silicon conducts electricity but is brittle like a non-metal. These elements blur the line between metals and non-metals.
Hydrogen: The Odd One OutHydrogen is placed on the left but is not a metal. It behaves mostly like a non-metal gas. Its position sometimes confuses beginners. Hydrogen’s unique traits make it a special case in the periodic table.
Transition Metals and Their VariationsTransition metals are in the middle of the table. They have different properties than typical left-side metals. Some show variable oxidation states. This makes their chemistry more complex and diverse.
Alkali Metals and ReactivityAlkali metals are very reactive and found on the extreme left. Their reactivity increases down the group. This high reactivity makes them behave differently from other metals. They rarely appear in pure form in nature.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Practical Importance Of Left-side Metals
Metals on the left side of the periodic table are key in many industries. They conduct electricity well and are used in wiring and tools. Their strength and flexibility make them useful for building and manufacturing.
Industrial Uses Of Left-side Metals
Metals on the left side of the periodic table play a big role in industries. These metals include lithium, sodium, potassium, and calcium. They are light and reactive, making them useful in many products. For example, lithium is key in batteries for phones and cars. Sodium and potassium help in making glass and soap. Calcium is vital for cement and steel production.
Role In Everyday Life
People use left-side metals daily without realizing it. Sodium is in table salt, essential for taste and health. Potassium helps plants grow and is found in fertilizers. Calcium is important for strong bones and teeth. These metals support many body functions and keep life running smoothly.
Importance In Technology
Left-side metals drive many modern technologies. Lithium powers rechargeable batteries in laptops and electric cars. Sodium vapor lamps light streets and stadiums efficiently. These metals help create lighter and faster devices. They also improve energy storage and reduce pollution.
Environmental Impact And Recycling
Mining left-side metals can harm the environment. Responsible use and recycling help reduce damage. Recycling lithium batteries saves resources and lowers waste. Using these metals wisely supports a cleaner planet. Efforts to recycle and reuse are growing worldwide.
Credit: periodictableguide.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Metals Mostly Found On The Left Side Of The Periodic Table?
Yes, most metals are located on the left side and center of the periodic table. These include alkali and alkaline earth metals, which are highly reactive and good conductors of electricity.
Why Are Alkali Metals On The Periodic Table’s Left Side?
Alkali metals are on the far left because they have one electron in their outer shell. This makes them highly reactive and eager to lose that electron to form positive ions.
Do Metals On The Left Side Have Similar Properties?
Yes, metals on the left side share traits like high conductivity, malleability, and reactivity. They typically lose electrons easily to form cations in chemical reactions.
Are Transition Metals Located On The Left Side Too?
Transition metals are found in the center of the periodic table but still lean toward the left side. They have variable oxidation states and are less reactive than alkali metals.
Conclusion
Metals mostly sit on the left side of the periodic table. They have few electrons in their outer shell. This makes them good at losing electrons and forming positive ions. These metals share common features like shine, malleability, and conductivity.
Understanding their position helps explain their behavior and uses. The left side metals play a big role in many industries. Their simple structure makes them easy to study and use. This knowledge helps in learning chemistry and material science.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.